In mathematics, a Mersenne prime is a prime number of the form  . They are named after the French monk Marin Mersenne who studied them in the early 17th century.
. They are named after the French monk Marin Mersenne who studied them in the early 17th century.
If n is a composite number then so is 2n − 1. The definition is therefore unchanged when written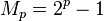 where p is assumed prime.
where p is assumed prime.
More generally, numbers of the form without the primality requirement are called Mersenne numbers. Mersenne numbers are sometimes defined to have the additional requirement that n be prime, equivalently that they bepernicious Mersenne numbers, namely those pernicious numbers whose binary representation contains no zeros. The smallest composite pernicious Mersenne number arises with p = 11.
without the primality requirement are called Mersenne numbers. Mersenne numbers are sometimes defined to have the additional requirement that n be prime, equivalently that they bepernicious Mersenne numbers, namely those pernicious numbers whose binary representation contains no zeros. The smallest composite pernicious Mersenne number arises with p = 11.
A double Mersenne number is a Mersenne number of the form
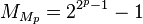
where p is a Mersenne prime exponent.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Numbers
{
long number;
Numbers(long n)
{
number=n;
}
boolean isMersenne(){
long n=0;
for(int i=1;i<=20;i++)
{
n=(long)(Math.pow(2,i)-1);
if(n==number){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
boolean isDoubleMersenne(){
long n=0;long pwr=0;
for(int i=1;i<=20;i++)
{
pwr=(long)Math.pow(2,i)-1;
n=(long)(Math.pow(2,pwr)-1);
if(n==number)
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
public void genMersenneNos(){
long num=0;
System.out.println("Generated Mersenne numbers are :");
for(int i=1;i<=10;i++)
{
num=(long)(Math.pow(2,i)-1);
System.out.print(num+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public void genDoubleMersenneNos()
{
long num=0;long pwr=0;
System.out.println("Generated double Mersenne Numbers are:");
for(int i=1;i<=6;i++)
{
pwr=(long)Math.pow(2,i)-1;
num=(long)(Math.pow(2,pwr)-1);
System.out.print(num+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[]args){
Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);
long n;
System.out.println("Enter a number");
n=in.nextLong();
Numbers numObject=new Numbers(n);
if(numObject.isDoubleMersenne()==true)
{
System.out.println(n+"is a double Mersenne Number");
numObject.genDoubleMersenneNos();
}
else if(numObject.isMersenne()==true)
{
System.out.println(n+"is a Mersenne Number");
numObject.genMersenneNos();
}
else
System.out.println(n+"is neither a Mersenne Number nor a Double Mersenne Number");
}
}
 . They are named after the French monk Marin Mersenne who studied them in the early 17th century.
. They are named after the French monk Marin Mersenne who studied them in the early 17th century.If n is a composite number then so is 2n − 1. The definition is therefore unchanged when written
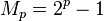 where p is assumed prime.
where p is assumed prime.More generally, numbers of the form
 without the primality requirement are called Mersenne numbers. Mersenne numbers are sometimes defined to have the additional requirement that n be prime, equivalently that they bepernicious Mersenne numbers, namely those pernicious numbers whose binary representation contains no zeros. The smallest composite pernicious Mersenne number arises with p = 11.
without the primality requirement are called Mersenne numbers. Mersenne numbers are sometimes defined to have the additional requirement that n be prime, equivalently that they bepernicious Mersenne numbers, namely those pernicious numbers whose binary representation contains no zeros. The smallest composite pernicious Mersenne number arises with p = 11.A double Mersenne number is a Mersenne number of the form
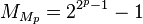
where p is a Mersenne prime exponent.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Numbers
{
long number;
Numbers(long n)
{
number=n;
}
boolean isMersenne(){
long n=0;
for(int i=1;i<=20;i++)
{
n=(long)(Math.pow(2,i)-1);
if(n==number){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
boolean isDoubleMersenne(){
long n=0;long pwr=0;
for(int i=1;i<=20;i++)
{
pwr=(long)Math.pow(2,i)-1;
n=(long)(Math.pow(2,pwr)-1);
if(n==number)
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
public void genMersenneNos(){
long num=0;
System.out.println("Generated Mersenne numbers are :");
for(int i=1;i<=10;i++)
{
num=(long)(Math.pow(2,i)-1);
System.out.print(num+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public void genDoubleMersenneNos()
{
long num=0;long pwr=0;
System.out.println("Generated double Mersenne Numbers are:");
for(int i=1;i<=6;i++)
{
pwr=(long)Math.pow(2,i)-1;
num=(long)(Math.pow(2,pwr)-1);
System.out.print(num+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[]args){
Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);
long n;
System.out.println("Enter a number");
n=in.nextLong();
Numbers numObject=new Numbers(n);
if(numObject.isDoubleMersenne()==true)
{
System.out.println(n+"is a double Mersenne Number");
numObject.genDoubleMersenneNos();
}
else if(numObject.isMersenne()==true)
{
System.out.println(n+"is a Mersenne Number");
numObject.genMersenneNos();
}
else
System.out.println(n+"is neither a Mersenne Number nor a Double Mersenne Number");
}
}
